Netskope products serve the purpose of security AND as tools to troubleshoot with. Tools that are often overlooked by everyone, including us!
In this article, we are going to cover one of our newest products acquired through the purchase and partnership of Infiot’s Borderless WAN (BWAN). BWAN is the technology commonly known as Software Defined Wide Area Networking (SD-WAN). We will answer the questions of:
- How does the Netskope Endpoint SD-WAN Client become a tool to be used?
- How am I able to use the Netskope Endpoint SD-WAN Client for displaying bypasses in the Netskope Endpoint SD-WAN console?
As a little background information, “Netskope BWAN extends the concept of network segmentation beyond traditional network perimeters, catering to the needs of a modern workforce that operates from varying locations and uses a multitude of devices. Netskope BWAN ensures network segmentation for any device by encapsulating each session in a secure and encrypted tunnel. This segmentation extends to all applications and data, whether hosted in the cloud or on-premises, effectively isolating critical resources from unauthorized access.” from https://www.netskope.com/blog/empowering-secure-cloud-adoption-a-response-to-the-nsa-and-cisa-cybersecurity-guidelines
How does Netskope Endpoint SD-WAN become a tool to be used?
There are three (3) steps to send traffic to the Netskope SD-WAN console.
- Bypass the Netskope Endpoint SD-WAN process/applications in the steering configuration.
- Bypass traffic at the Netskope NG-SWG Client level.
- Define interesting traffic for the Netskope Endpoint SD-WAN Client.
Netskope NG-SWG Client Steering Configuration
In order for the endpoint to process bypasses, bypass exceptions should be handled at the client will need to process them, see pic.
Bypassing the Netskope Endpoint SD-WAN 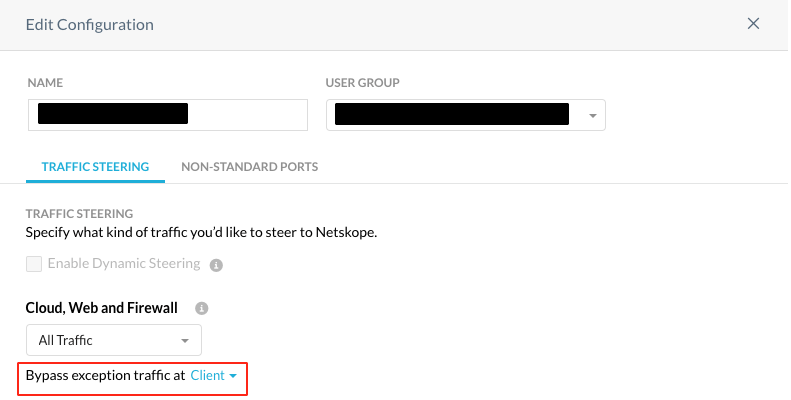
Processes/Applications
Since the Netskope Endpoint SD-WAN Processes/Applications are predefined it is a matter of selecting it from a list of applications and adding it to the steering configuration. The bypass here is needed to send traffic through to the SD-WAN console. Consider it similar to VPN processes which need to be bypassed for co-existence with the Netskope NG-SWG Client.
Bypassing Netskope NG-SWG Client Traffic
In order for traffic to traverse or use the Netskope Endpoint SD-WAN Client it must be bypassed at the Netskope NG-SWG Client level and have the Netskope Endpoint SD-WAN Client installed which tunnels all the bypassed traffic to the SD-WAN console. The Netskope Endpoint SD-WAN operates similarly to that of a VPN, in effect it is a VPN replacement meant for SD-WAN features, see above. To bypass traffic, we advise using the following recommendations for:
- Exception Configuration for VPN Applications
- Application Exceptions
- Category Exceptions
- SSL Certificate Pinned Applications
- Domain Exceptions
- DNS Exceptions
- Destination Locations
(When you want to send traffic to the SD-WAN console for traffic features, including it being used as a tool, you must NOT bypass traffic but steer to the Netskope console. When you bypass and steer traffic, this sends traffic through to the Netskope Client proxies not to the SD-WAN console. Traffic can be steered to the Netskope Client proxies after it arrives at the SD-WAN console, another use case for another time.)
Let’s define Microsoft Edge as an SSL Certificate Pinned Application which is to be bypassed at the Netskope NG-SWG Client. We are then going to send all traffic from Microsoft Edge to any and all destinations, as an example. This often happens with custom SSL Certificate Pinned applications.
Define the SSL Certificate Pinned Application
Bypassing in Steering
Defining Interesting Traffic for the Netskope Endpoint SD-WAN Client
Since the Netskope Endpoint SD-WAN Client is a VPN replacement, any traffic that is deemed “interesting” should be defined in an AppX policy. “Interesting” in this case is traffic that is defined as that which is to be sent to a Netskope Endpoint SD-WAN console, i.e. networks, remote hosts, and so on. In other words, if you don’t steer it, the traffic cannot be seen and thus make use of Netskope Endpoint SD-WAN Client advanced features. Bypassing traffic at the Netskope NG-SWG Client and not defining it as interesting traffic with the Netskope Endpoint SD-WAN Client in effect bypasses traffic altogether and goes directly to the destination. In other words, we need to have a destination defined for the Internet for the Netskope Endpoint SD-WAN to see it.
A sample AppX policy that is meant for the use case of “seeing” traffic destined for Microsoft Edge Browser on Windows is simply a matter of steering anything destined to the Internet in the AppX policy. In the AppX policy below, we are prioritizing Zoom traffic as High and the rest automatically.
Since we are steering all Internet traffic bypassed at the Netskope NG-SWG Client level, we will see any traffic that was bypassed at the Netskope NG-SWG Client.
How am I able to use the Netskope Endpoint SD-WAN Client for displaying bypasses in the Netskope Endpoint SD-WAN console?
After traffic is bypassed in the Netskope NG-SWG Client and sent to the Netskope Endpoint SD-WAN console, it may be viewed in Clients within the Manage section. After clicking on a client, choosing the processes tab, then specifying the length of time for review, the page will refresh to display relevant data.
Scroll down and a list of processes will be displayed; the default number of displayed processes is 5 and may be expanded up to 50.
On the right hand side of the page is a column called Flows #. Each of these numbers is a hyperlink to a list of flows for that specific processes listed. Using the example of MS Edge being bypassed, if I click on that process then the page will refresh below the table to display flow information or traffic statistics if you will.
The same may be done for applications seen by the Netskope Endpoint SD-WAN client. In this case, applications are those which are defined in the Netskope Endpoint SD-WAN which may correspond to SaaS applications. There are times where custom applications may be defined and which also may be found here.
Relevance and Use Cases
Custom SSL Certificate Pinned Applications
During the course of deploying Netskope NG-SWG Clients, sometimes bypasses are implemented to resolve production issues. This often happens when there are applications which need to be made into SSL Certificate Pinned applications as the labor needed to import our SSL certificates into the appropriate stores is too resource intensive, time is of the essence, or a combination thereof. Combine this with destinations used by the applications not being fully documented due to changes with the application, OS, and a myriad of other reasons to create a complex and ever changing environment. Examples of how or what we need to do for CLI tools and Netskope SSL Certificates as well as documentation on avoiding AWS CLI issues may be found below.
We can now safely bypass the SSL Certificate Pinned applications and analyze the traffic seen coming from this application. In turn, we are able to take the list of destinations and then statically define the destinations in the certificate pinned application.
Predefined SSL Certificate Pinned Applications
When a new Netskope Client Steering Profile is created, we have a laundry list of predefined list of SSL Certification Pinned applications which get added to the profile. These predefined SSL Certificate Pinned applications may be denoted by their colorful icons, see below.
Custom SSL Certificate Pinned applications only have a four gray square icon.
Mentioning the predefined SSL Certificate Pinned applications is relevant because they have been known to require adding additional destinations as well as creating new SSL Certificate Pinned applications to add new services or processes that need to reach out. For example, Apple has been known to add new processes in the Mac OS which reach out for updates. Therefore we need to add new destinations or an entirely new certificate pinned application.
With the Netskope Endpoint SD-WAN Client listening to the traffic bypassed at the Netskope NG-SWG Client, we are now able to see the new destinations and/or services/processes, in effect the overall communication streams on the endpoint.
Other Netskope NG-SWG Exceptions
This same procedure may be used to determine what services on the local machine might be sending traffic to category destinations. Subsequently, AppX rules may be created to give priority for various services or categories that are bypassed at the Netskope NG-SWG Client.
Resource Savings
Since we are able to determine what applications (SSL Certificate Pinned or otherwise), destinations, or categories are being bypassed and their destinations, we can apply restrictions in the Netskope NG-SWG or Netskope Endpoint SD-WAN Clients. These restrictions can be the manual assignment of bandwidth usage, steering to Netskope Proxies for analysis and potentially DLP, or a multitude of other functions related to security or the manipulation of traffic.
“Shadow IT”
“Shadow IT” has been bane of the existence for administrators, auditors, management, or anyone else concerned about it. We have a wealth of products that help bring it out of the shadows and into the light. One of those products is Cloud Exchange which has been well discussed at Netskope Risk Exchange Ecosystem: Combating Shadow IT
Netskope Endpoint SD-WAN can be added to the arsenal in effect bringing “Shadow IT” into the light, resulting in visibility of the applications or a variety of other bypasses.
In Summary
The Netskope Endpoint SD-WAN Client is much more than a VPN replacement. It becomes a tool that is capable of documenting the bypasses which are performed by the Netskope NG-SWG Client. It is capable of providing a graphical representation of traffic to aid administrators in taking control of endpoints and troubleshooting issues as they occur.








