This guide walks you through deploying a Python script as a secure, timer-triggered Azure Function. This function will run every five minutes to automatically create and synchronize IPsec tunnels and BGP configurations between your Netskope SD-WAN fabric and Microsoft's Entra Internet Access service.
Prerequisites
Before you begin, make sure you have the following:
- An Azure subscription with permissions to create Function Apps, App Registrations, and assign permissions.
- A Netskope One SD-WAN tenant with administrative access to generate API keys and manage edges.
- Tested on Netskope Gateway version R5.4.89
Part 1: Configure Microsoft Entra ID
First, you'll create an App Registration to organize permissions and get your Tenant ID.
- Go to Microsoft Entra: Log in to the Microsoft Entra admin center.
- Create App Registration:
- In the left menu, go to Entra ID > App registrations.
- Click + New registration.
- Name it something descriptive, like Netskope-Entra-SSE-Automation.
- Leave other options as default and click Register.
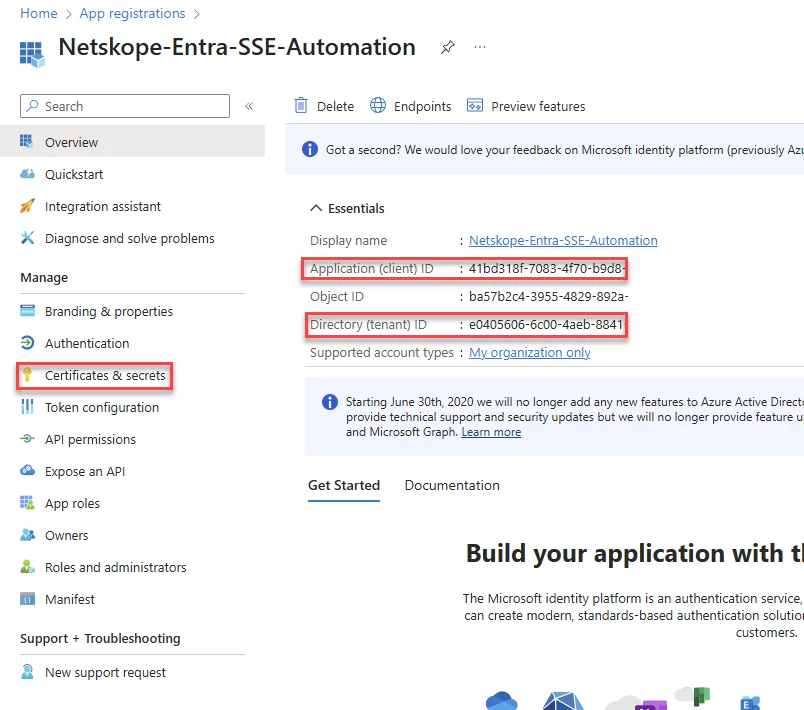
Record Tenant ID: On the app's Overview page (you might need to look under All applications), copy the Directory (tenant) ID and Application (client) ID. You will need this later.
Part 2: Configure Netskope One SD-WAN
Next, get the API credentials from your Netskope tenant and tag the SD-WAN edges you want to sync.
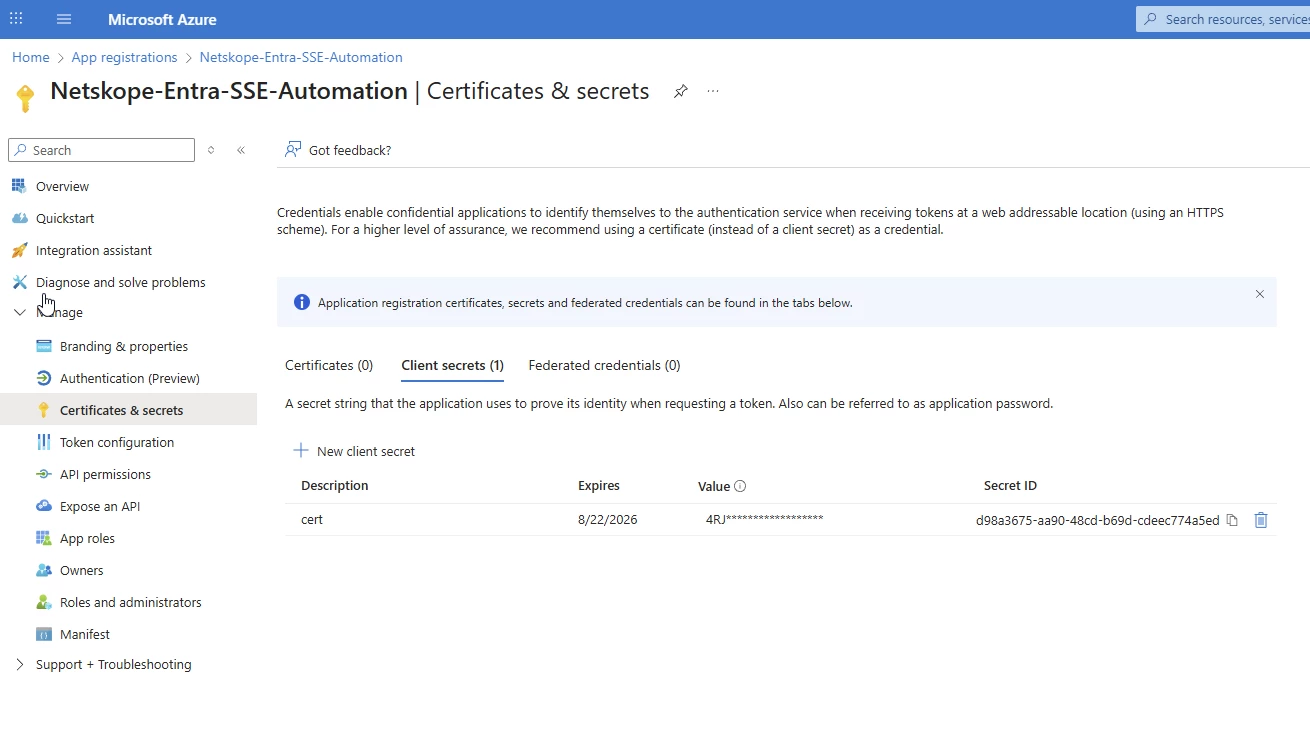
- Generate API Key:
- Log in to your Netskope One SD-WAN tenant.
- Go to Settings > API Tokens.
- Click Add New Token, name it (e.g., Azure-Function-Key),
Permissions needed
[
{
"rap_resource": "",
"rap_privs": [
"privVPNPeerCreate",
"privVPNPeerRead",
"privVPNPeerWrite",
"privVPNPeerDelete",
"privSiteRead",
"privSiteWrite"
]
}
]
- Immediately copy the generated API key. This is your Bearer Token.
- Note Your API URL:
- Identify your tenant's base URL by checking the URL while in your Gateway tenant. We will add ‘api’ to the url when adding it to Azure. It's typically https://<your-tenant-name>.api.infiot.com.
- Tag Your Edges:
- The script identifies which Netskope Edges to sync by looking for a specific tag.
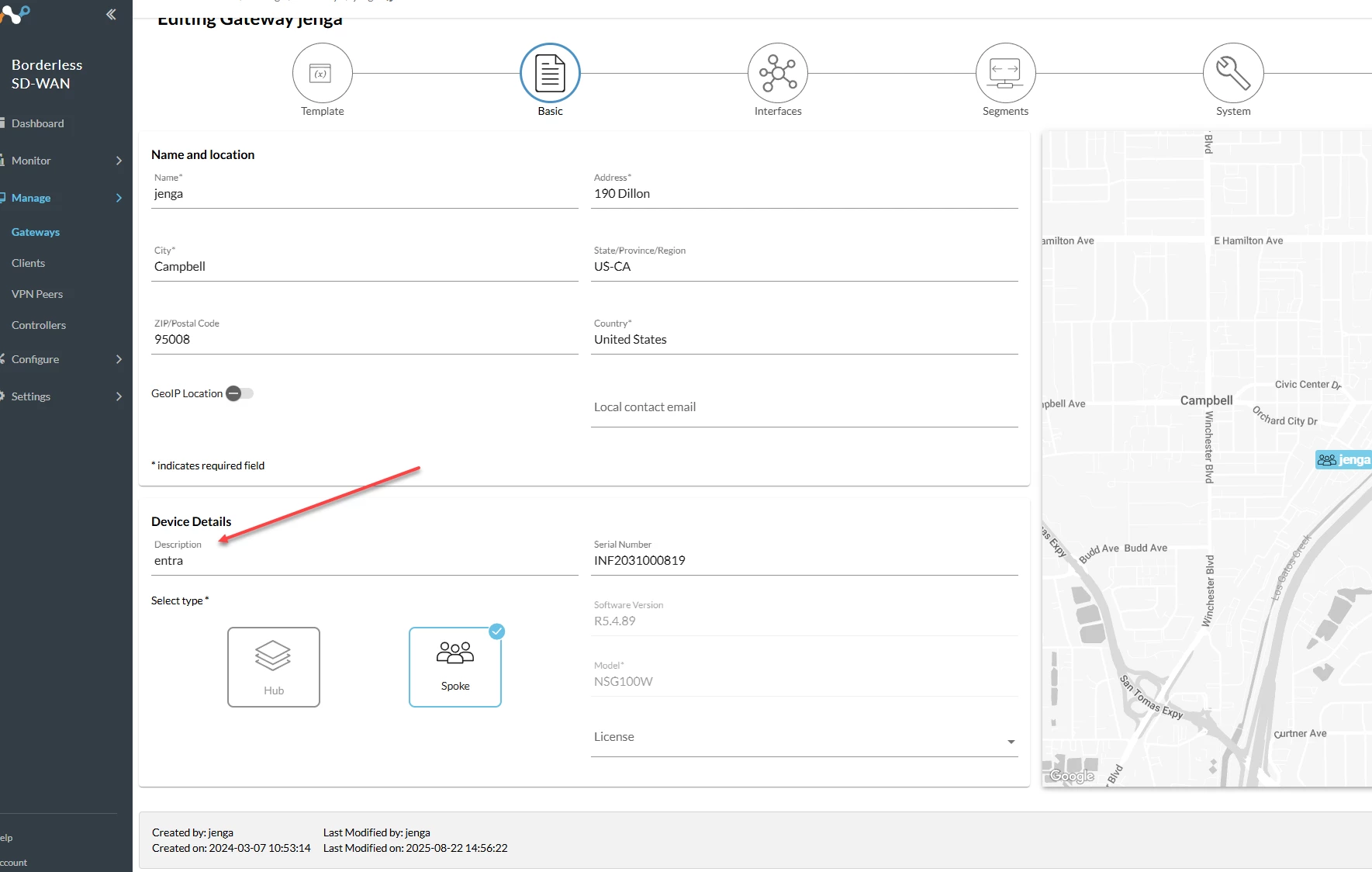
- For each Edge you want to connect to Entra, go to its settings and make sure its Description field contains the word entra (lowercase).
- The path for this is Manage > Gateways > Configure
Under the Basic tab
Part 3: Create & Configure the Azure Function App
This is where your automation script will live and run securely. We'll create the app, give it a passwordless identity, and grant it API permissions.
3.1 Create the Function App
- Go to the Azure Portal and search for Function App.
- Click + Create and fill out the details:
- Plan: Select Flex Consumption
- Resource Group: Create a new one (e.g., netskope-automation-rg).
- Function App name: Give it a unique name (e.g., netskope-entra-sync-function).
- Region: Choose a region near you.
- Runtime stack: Select Python (version 3.9 or newer).
- Instance size: 2048 MB
- Click Review + create, then Create.
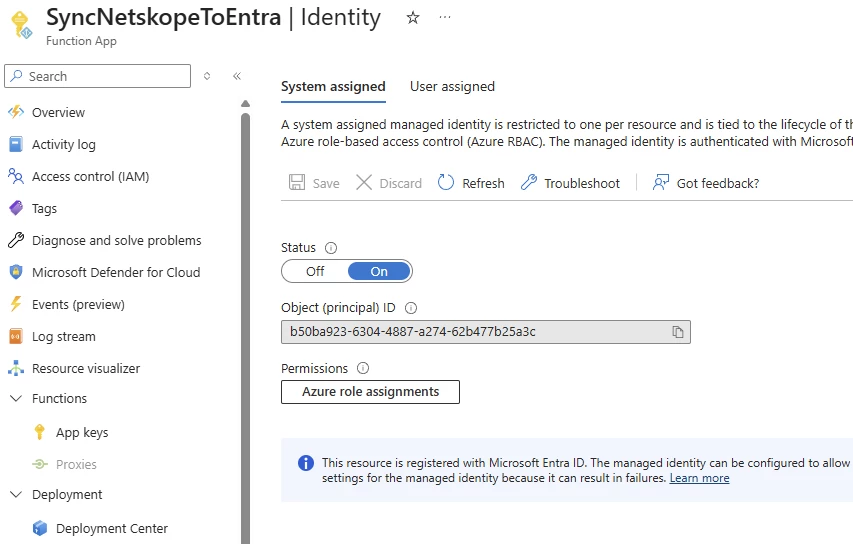
3.2 Enable System-Assigned Managed Identity
- Once deployed, go to your new Function App.
- In the left menu under Settings, click Identity.
- Select the System assigned tab, switch the Status to On, and click Save. This creates a secure, passwordless identity for your app in Entra ID.
- A pop-up will appear and you will need to select ‘Yes’ so that the application gets created in Entra. In the next step, you will add permissions for it.
3.3 ⚙️ Configure Application Settings
- Return to your Function App in the Azure Portal.
- Under Settings, click Environment variables.
- Under Application settings, click + New application setting to add these three key-value pairs. This securely stores your credentials outside of the code.
- Name: TENANT_ID Value: The Directory (tenant) ID you copied from Entra in Part 1.
- Name: INFRA_API_BASE_URL Value: Your Netskope API base URL from Part 2.
- Name: INFRA_API_BEARER_TOKEN Value: The Netskope API key you copied in Part 2.
- Name: CLIENT_ID Value: The client API key you copied in step 1
- Click Save to apply the new settings.
Part 4: Deploy the Automation Script
Create a Timer-Triggered Function:
- In your Function App, go to Overview, Functions and click + Create with VS Code or Editor.
- Follow the Microsoft directions to create and deploy https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-functions/how-to-create-function-vs-code?pivot=programming-language-python&pivots=programming-language-python
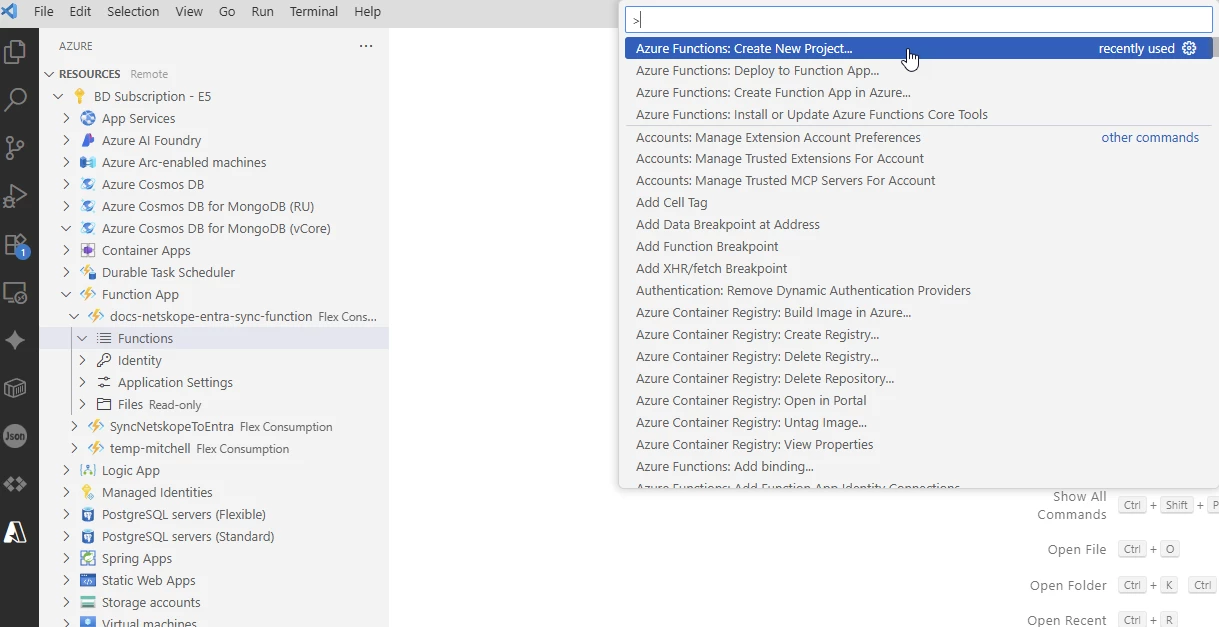
In VS Code
In VS Code with the Azure plugin.
Login and select the Function App that you created and hit F1. This should start the Command Palette. Type Azure Functions: Create a new project
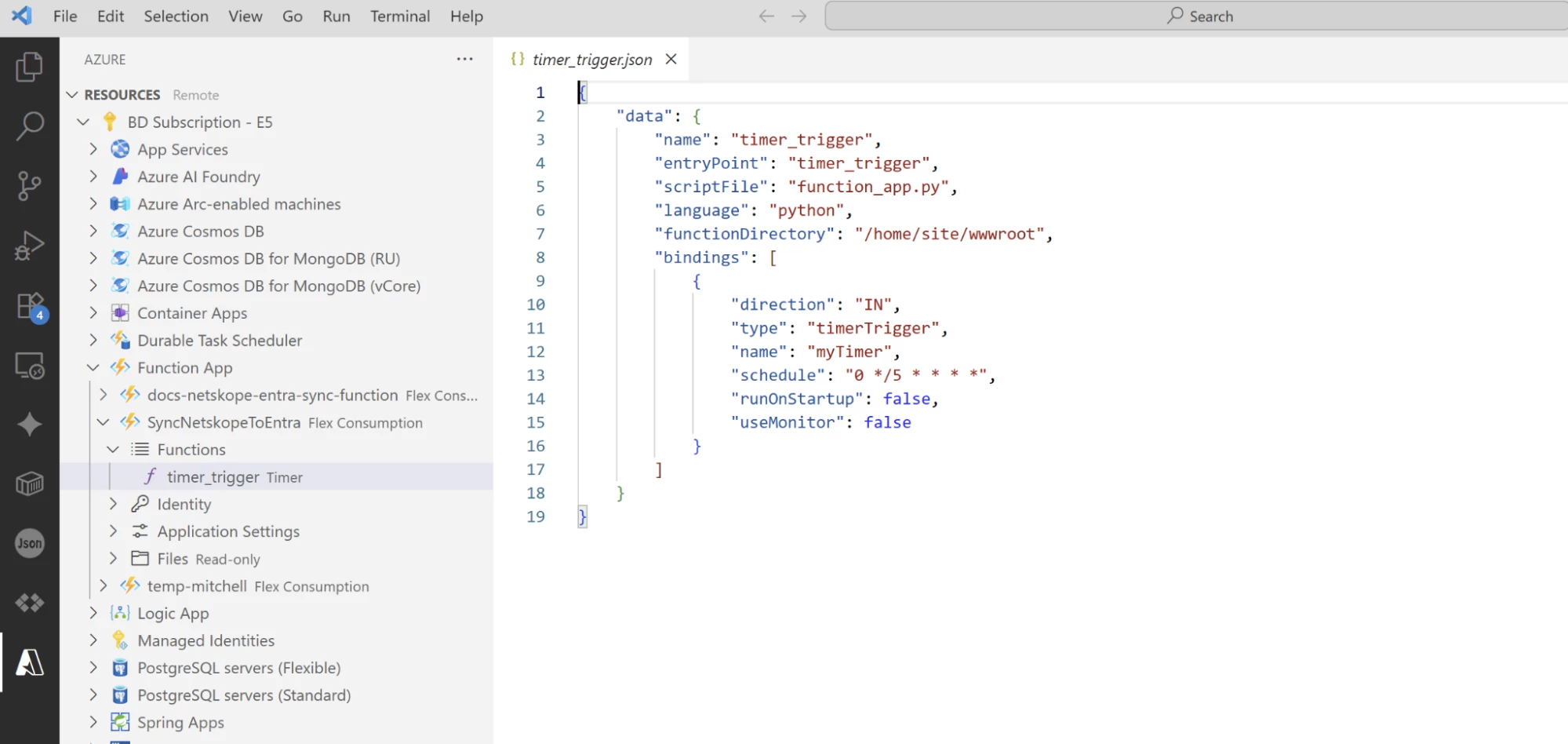
- Select a directory to save the project in. The name of the directory will end up being the name of your Function App
- Select Python 3.9 or newer
- Choose the Timer trigger template.
- Name the function timer_trigger.
- Set the Schedule to 0 * 5 * * * * to run every 5 minutes.
- Open in current window
- Commit
In VS Code create a new text file Paste in the code below
Save as (__init__.py):
Python
import atexit
import os
import msal
import requests
import json
import secrets
import string
import azure.functions as func
# --- Configuration (Loaded from Azure Function App Settings) ---
TENANT_ID = os.environ.get("TENANT_ID")
INFRA_API_BASE_URL = os.environ.get("INFRA_API_BASE_URL")
INFRA_API_BEARER_TOKEN = os.environ.get("INFRA_API_BEARER_TOKEN")
CLIENT_ID = os.environ.get("CLIENT_ID")
CLIENT_SECRET = os.environ.get("CLIENT_SECRET")
SCOPES = ["https://graph.microsoft.com/.default"]
GRAPH_BASE_ENDPOINT = "https://graph.microsoft.com/beta/networkAccess/connectivity/remoteNetworks"
# Use a single header definition for all Infiot API calls
INFRA_API_HEADERS = {
"Authorization": f"Bearer {INFRA_API_BEARER_TOKEN}",
"Content-Type": "application/json"
}
# --- Infiot API Functions ---
def list_all_edges():
"""Lists all edges for a specific tenant using the Infiot API."""
api_url = f"{INFRA_API_BASE_URL}/edges"
try:
response = requests.get(api_url, headers=INFRA_API_HEADERS)
response.raise_for_status()
return response.json()
except Exception as err:
print(f"An Infiot API error occurred while listing edges: {err}")
return None
def get_public_ip_from_gateway(gateway_object):
"""Parses the IP address from the GE1 interface of a gateway object."""
try:
for interface in gateway_object.get('interfaces', []):
if interface.get('name') == 'GE1':
addresses = interface.get('addresses', [])
if addresses and addresses[0].get('address'):
return addresses[0].get('address')
except (KeyError, IndexError) as e:
print(f"Error parsing gateway object for GE1 IP: {e}")
return None
def get_vpn_peers():
api_url = f"{INFRA_API_BASE_URL}/vpnpeers"
print(f"\nSTEP: Getting VPN peers from Infiot …")
try:
response = requests.get(api_url, headers=INFRA_API_HEADERS, timeout=30)
response.raise_for_status()
return response.json()
except requests.exceptions.HTTPError as err:
print(f"❌ FAILED to get VPN peers: {err.response.text}")
except Exception as err:
print(f"An Infiot API error occurred while fetching VPN peers: {err}")
return None
def create_vpn_peer(payload):
"""Creates a new VPN peer in Infiot."""
api_url = f"{INFRA_API_BASE_URL}/vpnpeers"
print(f"\nSTEP: Creating Infiot VPN Peer for {payload['ip_address']}...")
print("Request Body:")
print(json.dumps(payload, indent=2))
try:
response = requests.post(api_url, headers=INFRA_API_HEADERS, data=json.dumps(payload))
response.raise_for_status()
print("✅ Success! VPN Peer created in Infiot.")
return response.json()
except requests.exceptions.HTTPError as err:
print(f"❌ FAILED to create VPN peer: {err.response.text}")
except Exception as err:
print(f"An error occurred while creating VPN peer: {err}")
return None
def update_edge_by_id(edge_id, update_data, child_tenant_id=None):
"""
Updates an Infiot edge identified by ``edge_id`` using the PUT /edges/{id}
endpoint. Supply ``update_data`` following the UpdateEdgeInput schema (e.g.
including ``bgpConfiguration`` and ``staticRoutes``) to configure BGP peers
or static routes. When accessing the API with a Master MSP/MSP token,
specify ``child_tenant_id``; otherwise leave it ``None``.
"""
api_url = f"{INFRA_API_BASE_URL}/edges/{edge_id}"
params = {"childTenantId": child_tenant_id} if child_tenant_id else None
try:
response = requests.put(
api_url,
headers=INFRA_API_HEADERS,
params=params,
json=update_data,
)
response.raise_for_status()
return response.json()
except requests.exceptions.HTTPError as err:
print(f"❌ FAILED to update edge {edge_id}: {err.response.text}")
except Exception as err:
print(f"An error occurred while updating edge {edge_id}: {err}")
return None
# --- Microsoft Graph API Functions ---
def get_all_remote_networks(graph_headers):
"""Retrieves all remote networks and their device links, handling pagination."""
all_networks = []
endpoint = f"{GRAPH_BASE_ENDPOINT}?$expand=deviceLinks"
print("Gathering existing remote networks and device links from Microsoft Entra...")
while endpoint:
try:
response = requests.get(endpoint, headers=graph_headers)
response.raise_for_status()
data = response.json()
all_networks.extend(data.get("value", []))
endpoint = data.get("@odata.nextLink")
except requests.exceptions.HTTPError as err:
print(f"❌ FAILED to get remote networks: {err.response.text}")
return None
print(f"Successfully gathered details for {len(all_networks)} networks.")
return all_networks
def create_minimal_remote_network(graph_headers, name, region):
"""Creates a simple remote network."""
body = {"name": name, "region": region}
print(f"STEP 1: Creating minimal remote network '{name}'...")
try:
response = requests.post(GRAPH_BASE_ENDPOINT, headers=graph_headers, data=json.dumps(body))
response.raise_for_status()
print("✅ Step 1 Succeeded.")
return response.json()
except requests.exceptions.HTTPError as err:
print(f"❌ Step 1 FAILED: {err.response.text}")
return None
def add_device_link(graph_headers, network_id, device_link_payload):
"""Adds a device link to an existing remote network."""
endpoint = f"{GRAPH_BASE_ENDPOINT}/{network_id}/deviceLinks"
print(f"\nSTEP 2: Adding device link to network ID {network_id}...")
try:
response = requests.post(endpoint, headers=graph_headers, data=json.dumps(device_link_payload))
response.raise_for_status()
print(f"✅ Step 2 Succeeded with Status Code: {response.status_code}")
return True
except requests.exceptions.HTTPError as err:
print(f"❌ Step 2 FAILED: {err.response.text}")
return False
# --- Main Script ---
if __name__ == "__main__":
cache = msal.SerializableTokenCache()
atexit.register(
lambda: open("my_token_cache.bin", "w").write(cache.serialize())
if cache.has_state_changed else None
)
try:
cache.deserialize(open("my_token_cache.bin", "r").read())
except IOError:
pass
# 3. Create the ConfidentialClientApplication.
app = msal.ConfidentialClientApplication(
client_id=CLIENT_ID,
client_credential=CLIENT_SECRET, # None works for a managed identity
authority=f"https://login.microsoftonline.com/{TENANT_ID}",
token_cache=cache
)
# 4. Acquire a token for Microsoft Graph (no user, no browser).
token_response = app.acquire_token_for_client(SCOPES)
# 5. Check that we got a token.
if not token_response or "access_token" not in token_response:
raise RuntimeError("Could not acquire Microsoft Graph access token")
print("✅ Microsoft Graph authentication successful.\n")
# 6. Prepare Graph headers for subsequent calls.
graph_access_token = token_response["access_token"]
graph_headers = {
"Authorization": f"Bearer {graph_access_token}",
"Content-Type": "application/json"
}
existing_networks_initial = get_all_remote_networks(graph_headers)
if existing_networks_initial is None:
exit()
existing_public_ips = {
link["ipAddress"]
for network in existing_networks_initial
for link in network.get("deviceLinks", [])
if link.get("ipAddress")
}
print(f"Found {len(existing_public_ips)} existing public IPs in Entra.\n")
infiot_response = list_all_edges()
if not infiot_response or 'data' not in infiot_response:
print("❌ Could not retrieve valid data from Infiot API. Exiting.")
exit()
# Initialise a lookup for pre-shared keys generated for each gateway
edge_psks = {}
# Filter the edges to those whose description contains 'entra'
entra_gateways = [
edge for edge in infiot_response.get('data', [])
if edge.get('description') and 'entra' in edge['description'].lower()
]
if not entra_gateways:
print("ℹ️ No Infiot gateways with 'Entra' in their description were found.")
else:
print(f"Found {len(entra_gateways)} Infiot gateways to process for Entra.\n")
for gateway in entra_gateways:
infiot_gateway_name = gateway.get('name')
print(f"--- Processing Infiot Gateway: {infiot_gateway_name} ---")
target_public_ip = get_public_ip_from_gateway(gateway)
if not target_public_ip:
print(f"❌ SKIPPING: Could not find a valid IP on the GE1 interface for gateway '{infiot_gateway_name}'.\n")
continue
if target_public_ip in existing_public_ips:
print(f"✅ SKIPPING: Remote network with public IP '{target_public_ip}' already exists in Entra.\n")
continue
print(f"ℹ️ No network found in Entra with public IP '{target_public_ip}'. Starting creation workflow.")
overlay_ip = gateway.get('overlayConfiguration', {}).get('ip')
if not overlay_ip:
print(f"❌ SKIPPING: Could not find overlay IP for gateway '{infiot_gateway_name}'.\n")
continue
network_name = f"{infiot_gateway_name}-Entra-{secrets.token_hex(2)}"
remote_network = create_minimal_remote_network(graph_headers, network_name, "eastUS")
if remote_network:
preshared_key = ''.join(secrets.choice(string.ascii_letters + string.digits) for _ in range(32))
edge_psks[infiot_gateway_name] = preshared_key
device_link_body = {
"name": f"{network_name}-Link",
"ipAddress": target_public_ip,
"deviceVendor": "other",
"bandwidthCapacityInMbps": "mbps1000",
"bgpConfiguration": {
"localIpAddress": "169.254.30.1",
"peerIpAddress": overlay_ip,
"asn": 400
},
"redundancyConfiguration": {"redundancyTier": "noRedundancy"},
"tunnelConfiguration": {
"@odata.type": "#microsoft.graph.networkaccess.tunnelConfigurationIKEv2Default",
"preSharedKey": preshared_key
}
}
link_creation_succeeded = add_device_link(graph_headers, remote_network.get("id"), device_link_body)
if link_creation_succeeded:
existing_public_ips.add(target_public_ip)
print(f"--- Finished Processing Infiot Gateway: {infiot_gateway_name} ---\n")
# --- Stage 2: Final Sync from Entra TO Infiot vpnpeers ---
print("\n--- Starting Final Sync: Entra Remote Networks to Infiot VPN Peers ---")
final_entra_networks = get_all_remote_networks(graph_headers)
infiot_vpn_peers = get_vpn_peers()
if final_entra_networks is None or infiot_vpn_peers is None:
print("❌ Cannot perform final sync due to errors fetching data. Exiting.")
exit()
existing_peer_ips = {peer.get('ip_address') for peer in infiot_vpn_peers.get('data', [])}
print(f"Found {len(existing_peer_ips)} existing VPN Peers in Infiot.")
for network in final_entra_networks:
if not network.get("deviceLinks"):
continue
network_name = network.get("name")
public_ip = network["deviceLinks"][0].get("ipAddress")
if not public_ip:
continue
print(f"\nChecking Entra network '{network_name}' with IP '{public_ip}'...")
if public_ip in existing_peer_ips:
print(f"✅ SKIPPING: VPN Peer for IP '{public_ip}' already exists in Infiot.")
else:
print(f"ℹ️ VPN Peer for IP '{public_ip}' not found in Infiot. Creating it...")
vpn_peer_payload = {
"name": network_name,
"description": f"Auto-created from Entra network '{network_name}'",
"ip_address": public_ip,
"type": "IKEV2",
"ikev2": {
"dh_group": 14,
"dpd_timeout": 60,
"encryption": "AES_GCM_256",
"hash": "SHA2_256",
"ike_sa_lifetime": 28800,
"ipsec_sa_lifetime": 28800,
"pfs": False,
},
"ip_location": False,
"location": {"lat": 37.9134, "lng": -122.03786}
}
create_vpn_peer(vpn_peer_payload)
# --- Stage 3: Add static route and BGP peer to the Entra SSE service ---
infiot_gateways_by_name = {gw.get('name'): gw for gw in infiot_response.get('data', []) if gw.get('name')}
print("\n--- Stage 3: Adding static route and BGP configuration to Infiot gateways ---")
for network in final_entra_networks:
name = network.get('name', '')
if '-Entra-' not in name or not network.get('deviceLinks'):
continue
gateway_name = name.split('-Entra-')[0]
gateway = infiot_gateways_by_name.get(gateway_name)
if not gateway:
continue
overlay_ip = gateway.get('overlayConfiguration', {}).get('ip')
if not overlay_ip:
print(f"⚠️ Unable to add BGP/static route: no overlay IP for gateway '{gateway_name}'.")
continue
device_link = network['deviceLinks'][0]
bgp_cfg = device_link.get('bgpConfiguration', {})
neighbor_ip = bgp_cfg.get('localIpAddress')
remote_as = bgp_cfg.get('asn')
if not neighbor_ip or remote_as is None:
print(f"⚠️ Missing neighbor IP/ASN for network '{name}', skipping.")
continue
update_payload = {
**({"psk": edge_psks.get(gateway_name)} if edge_psks.get(gateway_name) else {}),
"BgpConfiguration": [
{
"Name": f"SSE-BGP-{neighbor_ip}",
"Neighbor": neighbor_ip,
"RouterId": overlay_ip,
"RemoteAS": remote_as,
"LocalAS": 400,
"IsBfdEnabled": False
}
],
"StaticRoutes": [
{
"device": "auto",
"nhop": overlay_ip,
"destination": f"{neighbor_ip}/32",
"cost": 0,
"advertise": True,
"install": True
}
]
}
print(f"Adding BGP/static route on gateway '{gateway_name}' (edge ID {gateway.get('id')})...")
result = update_edge_by_id(gateway.get('id'), update_payload)
if result:
print(f"✅ Successfully updated edge '{gateway_name}' with BGP/static route settings.")
else:
print(f"❌ Failed to update edge '{gateway_name}'.")Add Dependencies (requirements.txt):
- In the local working directory on your computer, open requirements.txt in VS Code. Note: if you select it from the tree in VSC, it will tell you that it is read-only. So, you have to open it and then save before you deploy to function app.
- Delete all existing content and replace it with these three lines:
azure-functions
requests
azure-identity
When done, Deploy to Function App
You will now see the function in your Function App.
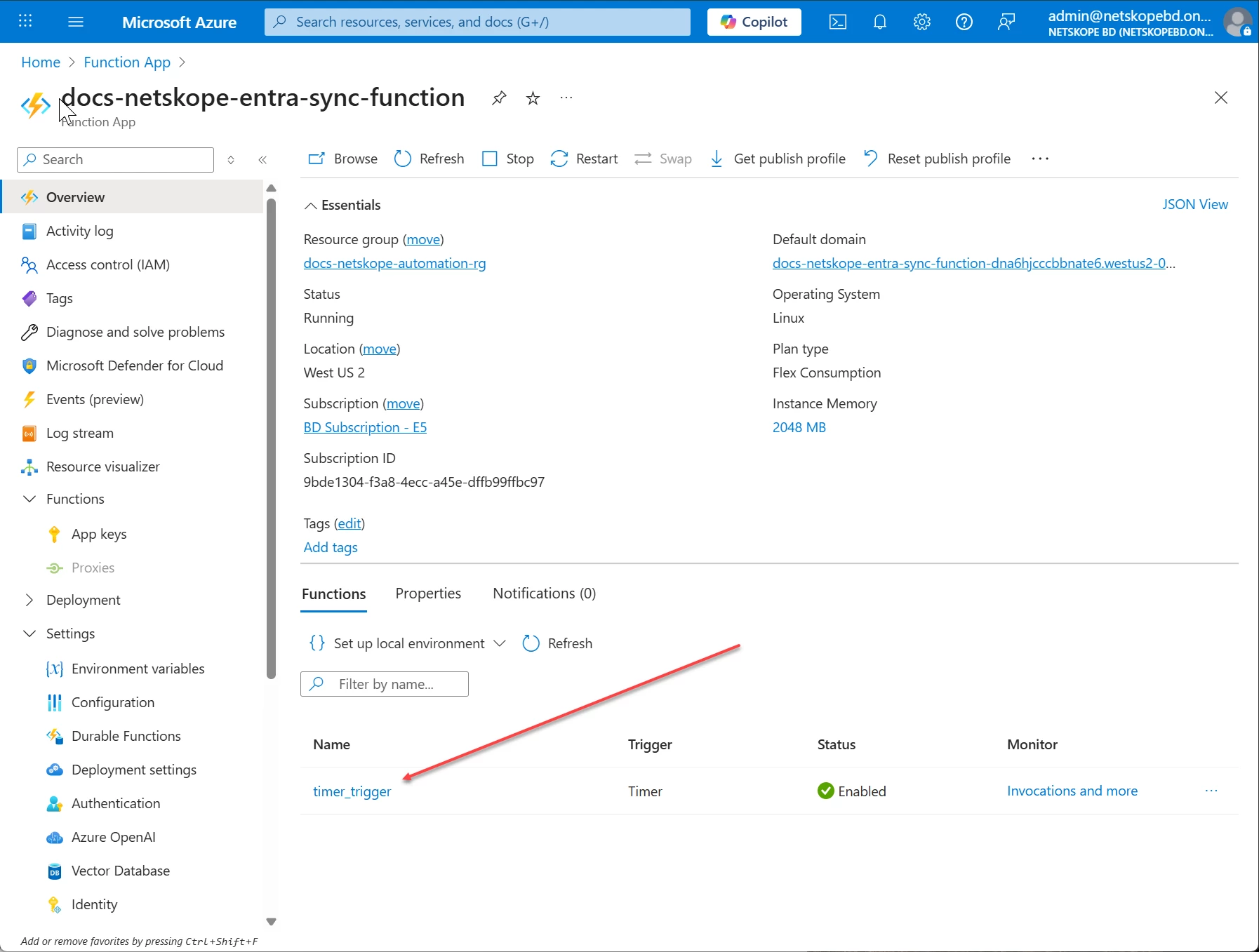
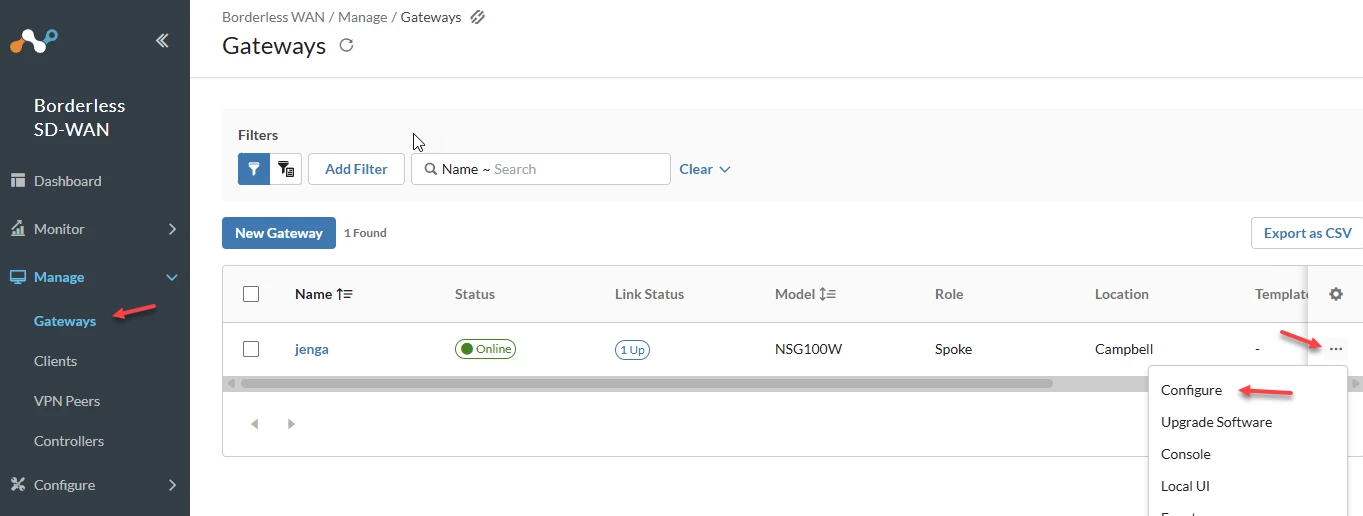
Finally, navigate to the Netskope BWAN portal and select the Gateways you want to associate the VPN peer that was automatically created to. Select the 3 dots and click Configure: (see screenshot)
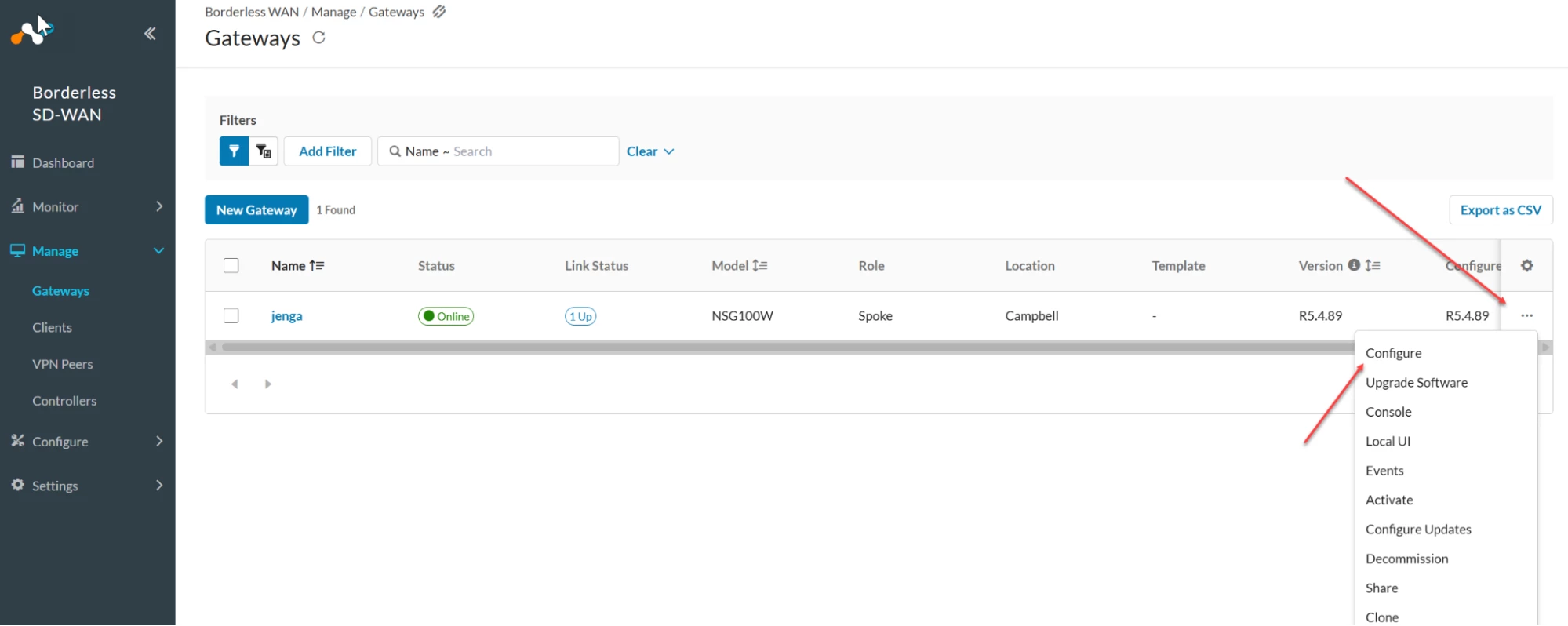
- Now navigate to Segments:
- Select the appropriate segment:
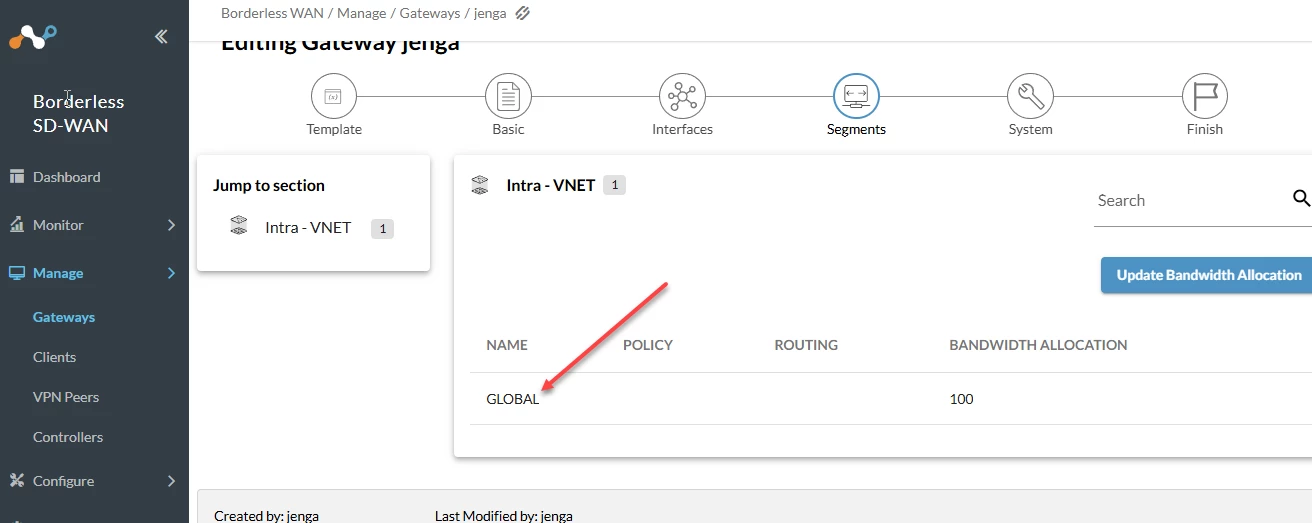
- Scroll down a select add VPN Peer
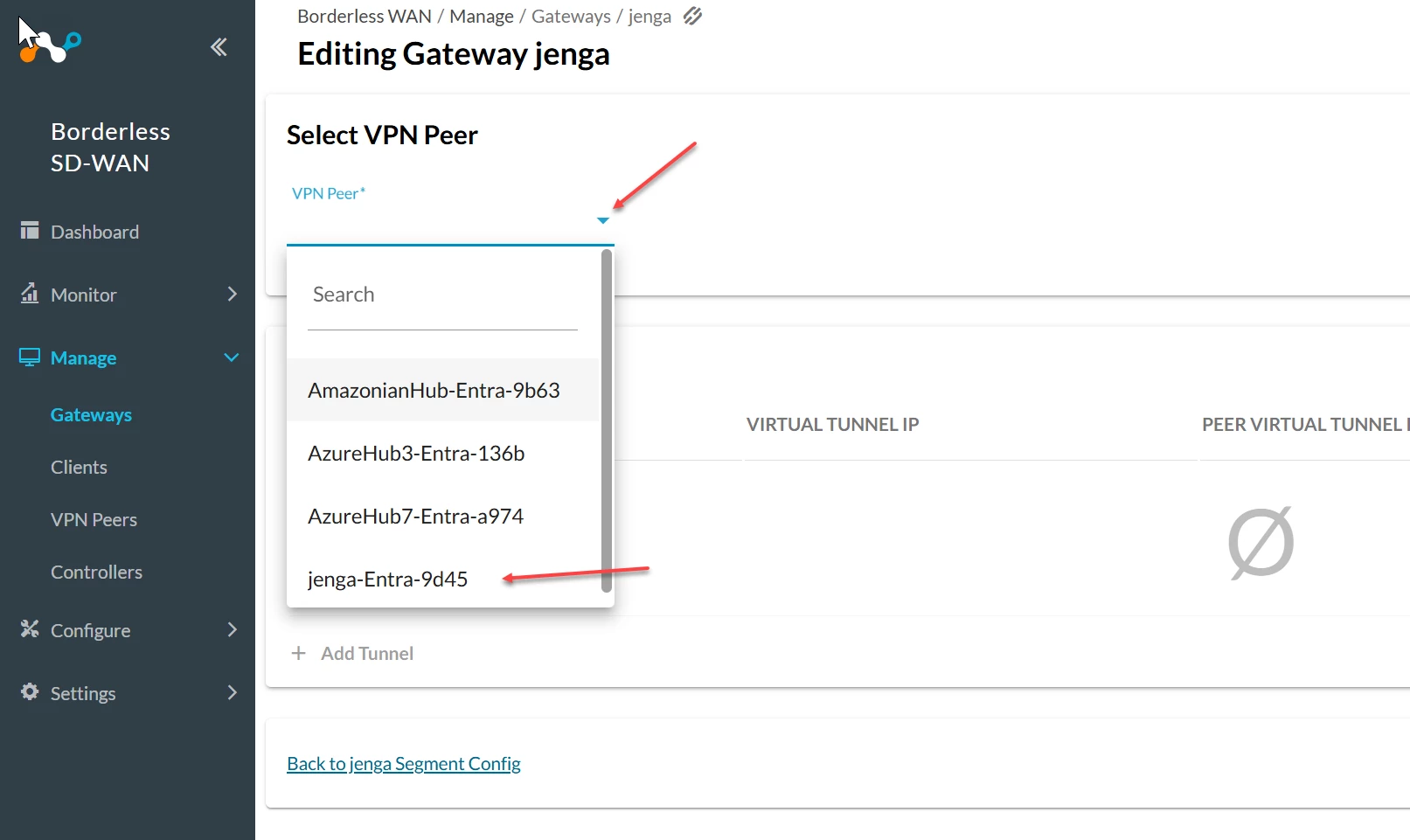
- Finally select the VPN Peer that matches the Gateway name. (this will be obvious)
Part 5: Monitor and Verify
Your automation is now deployed. Here’s how to check that it's working correctly.
- Check Function Logs:
- In your function's menu, select Monitor. You will see a list of recent executions (Invocations).
- Click on a recent timestamp to see the detailed logs for that run. Look for success messages or any errors.
- Verify in Entra ID:
- Go to Global Secure Access (Preview) > Connect > Remote Networks. You should see new networks created for your tagged Netskope edges.
- Verify in Netskope:
- Go to Configuration > VPN Peers. You should see new VPN peers that correspond to the remote networks created in Entra.





