Overview
Some environments using Netskope Client may encounter SSL or certificate validation issues when running Google Cloud CLI (gcloud) commands.
This happens because gcloud relies on its own embedded cacert.pem bundle (under the SDK’s certifi package), which doesn’t automatically include enterprise root certificates — such as Netskope’s Root CA.
Important note about bypassing *.googleapis.com
In many enterprise deployments administrators add bypass rules for *.googleapis.com (so some Google APIs are sent directly to Google). However, simply configuring core/custom_ca_certs_file with only the Netskope root certificate — or relying only on the Netskope root in a custom bundle — frequently does not resolve SSL errors for these bypassed domains.
Why this happens (observed behaviour):
After a bypass, the TLS connection may be negotiated directly with Google (or with different certificate chains), or the client and the SDK may expect the full set of public root CAs. If only the Netskope root is supplied to the SDK or core/custom_ca_certs_file, the SDK may still reject the handshake because the expected public CA chain is missing or the certificate chain seen by the process differs from the one used during inspection.
As a result, SSL/TLS errors may persist even though the Netskope root is present in a single custom file.
Script Purpose
This PowerShell script:
- Verifies administrative privileges and re-launches itself with elevated permissions if needed.
- Locates the correct cacert.pem file within the GCloud SDK installation.
- Backs up the original certificate bundle with a timestamp.
- Appends the Netskope Root CA to the end of the Google CLI cacert.pem file.
- Adds a timestamped marker for easy identification and rollback.
- Create the system variable REQUESTS_CA_BUNDLE with all the rootCAs in that machine , including Netskope rootCA.
This approach avoids the use of a static certificate bundle containing only the Netskope certificate. Consequently, even if you ignore googleapis.com, the Gcloud CLI should works as expected, just like all other Python-based command-line tools (since we are also creating the REQUESTS_CA_BUNDLE variable with a certificate bundle for all the root CAs in the system).
How to Run:
- Unzip the file
- Open Powershell as administrator
- CD to the folder the script is (example: cd "c:\temp")
- Move the Netskope rootCA to the same folder the script is located
- Execute .\netskope_cli_tools.ps1 -DestinationFolder <the folder you want to store the combinedBundle> (this folder will be used to create the REQUESTS_CA_BUNDLE system variable)
- Confirm that the output of the script looks like the image below:
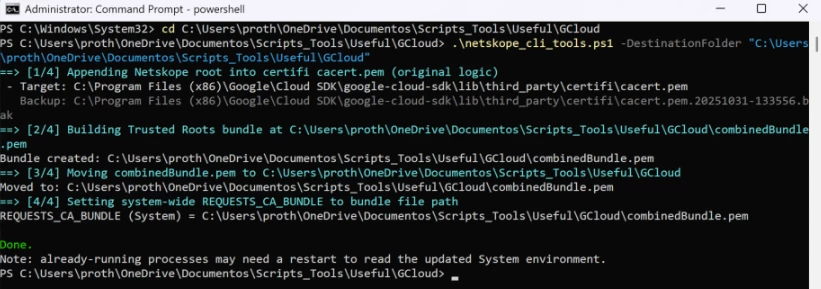
After completion, the Netskope root certificate authority (rootCA) will be attached to the Google SDK certificate bundle, and the REQUESTS_CA_BUNDLE variable will be modified/created, with the "DestinationFolder" defined in step 5.
(Full script available attached.)
Attention: this process is only for Windows machines.







