
 Netskope Global Technical Success (GTS)
Netskope Global Technical Success (GTS)
Block Websocket (WSS) Traffic
Netskope Cloud Version - 132
Objective
How to block Websocket Traffic via using Netskope Realtime Protection Policy
Prerequisite
Netskope SWG or NG-SWG license is required
Context
There are many applications on the internet where the initial traffic begins as HTTPS but later switches to a WebSocket connection. Some customers may have a business use case to block WebSocket traffic. This document explains how to achieve this using a Netskope Realtime Protection Policy.
Do You Know?
Before we proceed further, there are a few important details about WebSockets that you should be aware of -
| Protocol | Meaning | Security | Similar To | Works on Port Number |
| ws:// | WebSocket | No encryption | http:// | 80 |
| wss:// | WebSocket Secure | Encrypted (TLS/SSL) | https:// | 443 |
- wss:// stands for WebSocket Secure.
- It is the encrypted and secure version of the WebSocket protocol (ws://)
- WebSockets allow real-time, two-way communication between a browser (or client) and a server. Unlike HTTP, which requires a request/response each time, WebSockets keep a persistent connection open.
Sample
wss://example.com/socket
This means the browser is opening a secure WebSocket connection to the server at example.com
- Many applications on the internet switch their connection from HTTPS to WSS. One such application is Copilot on the https://www.bing.com/ page.
- Access https://www.bing.com/
- Click Copilot
- Traffic goes to https://copilot.microsoft.com
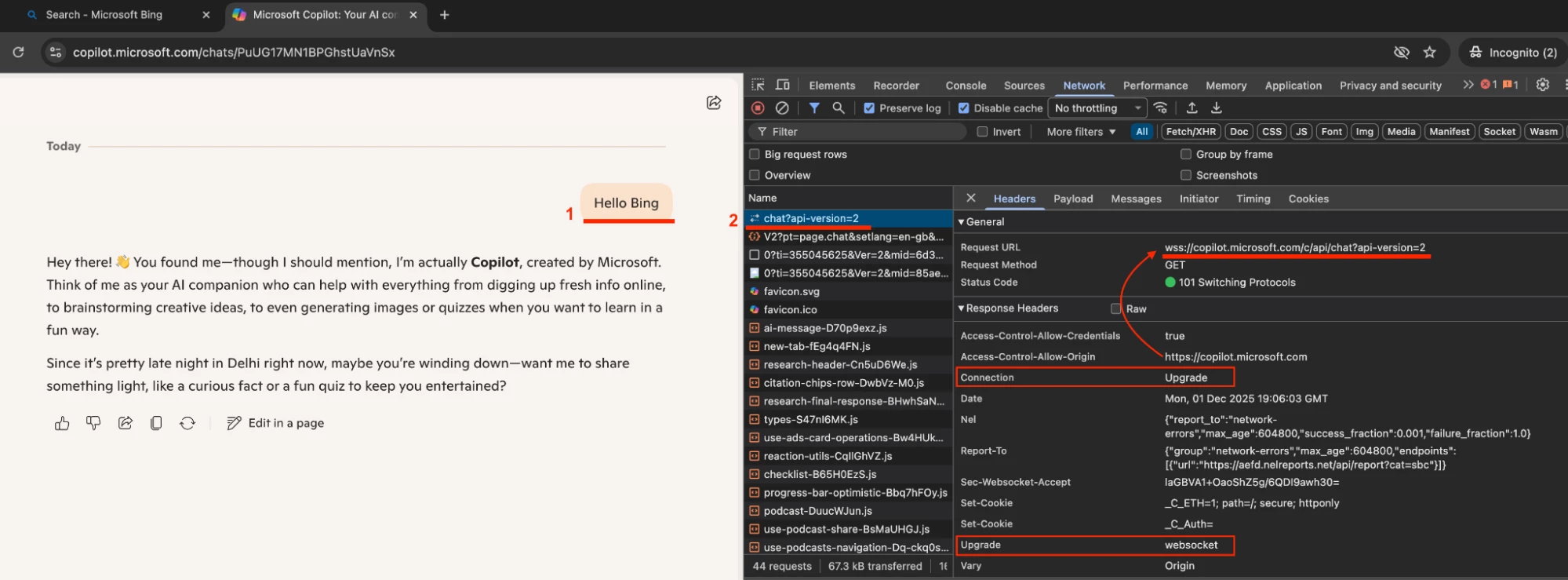
- Traffic switches from https:// to wss:// - wss://copilot.microsoft.com/c/api/chat?api-version=2
| Request URL | wss://copilot.microsoft.com/c/api/chat?api-version=2 | |
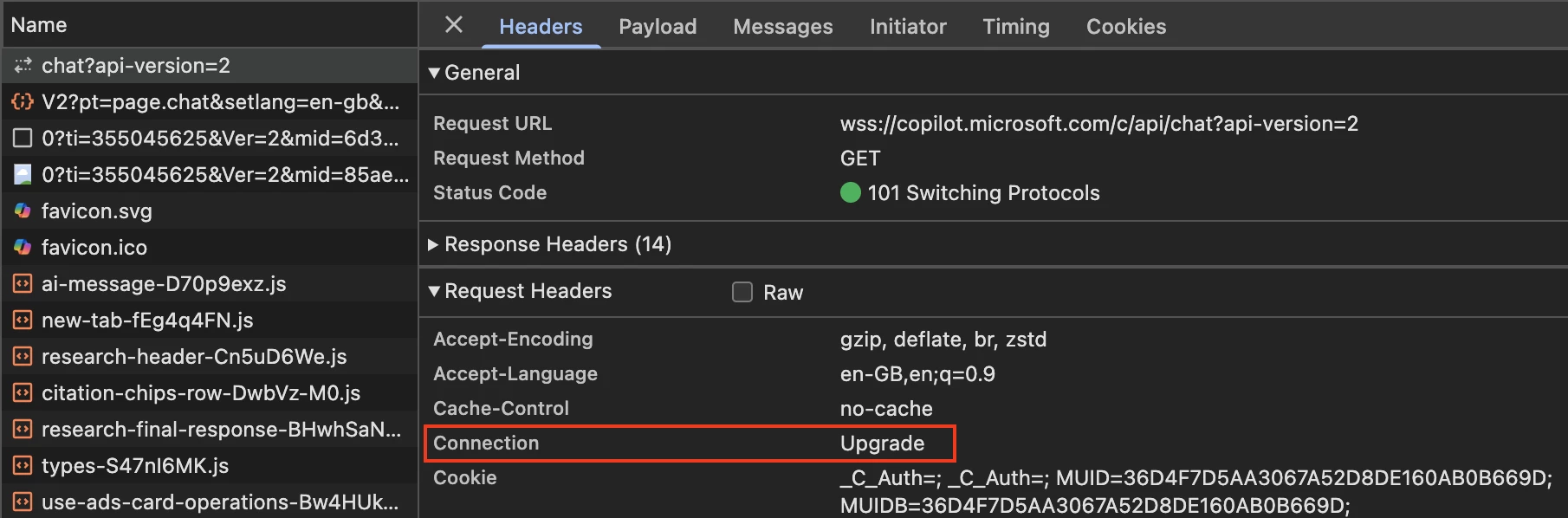
| Request Header | Connection - Upgrade | Upgrade - websocket |
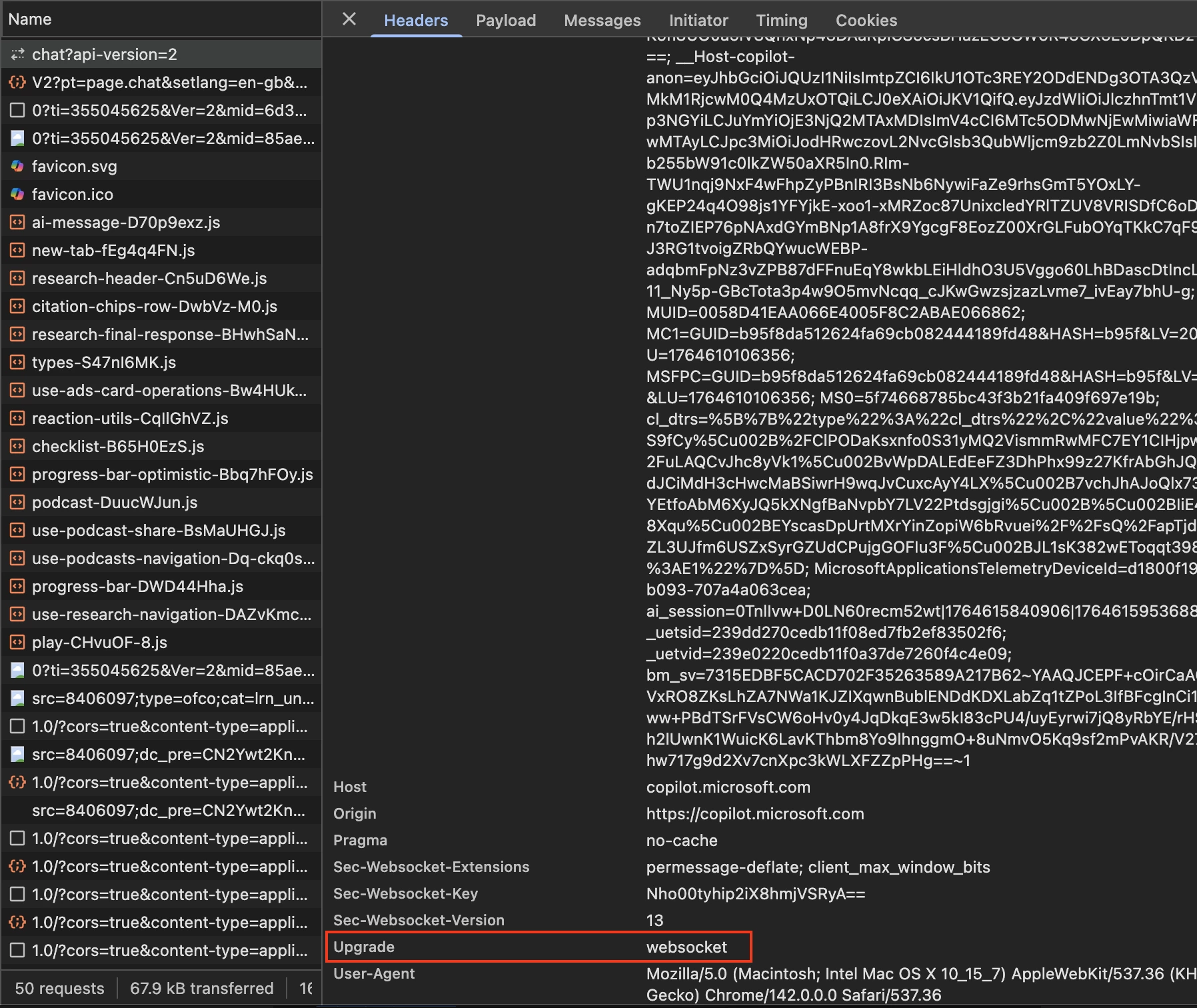
| Response Header | Connection - Upgrade | Upgrade - websocket |

- Let’s discuss how to restrict such connection switches in the next section.
Configuration
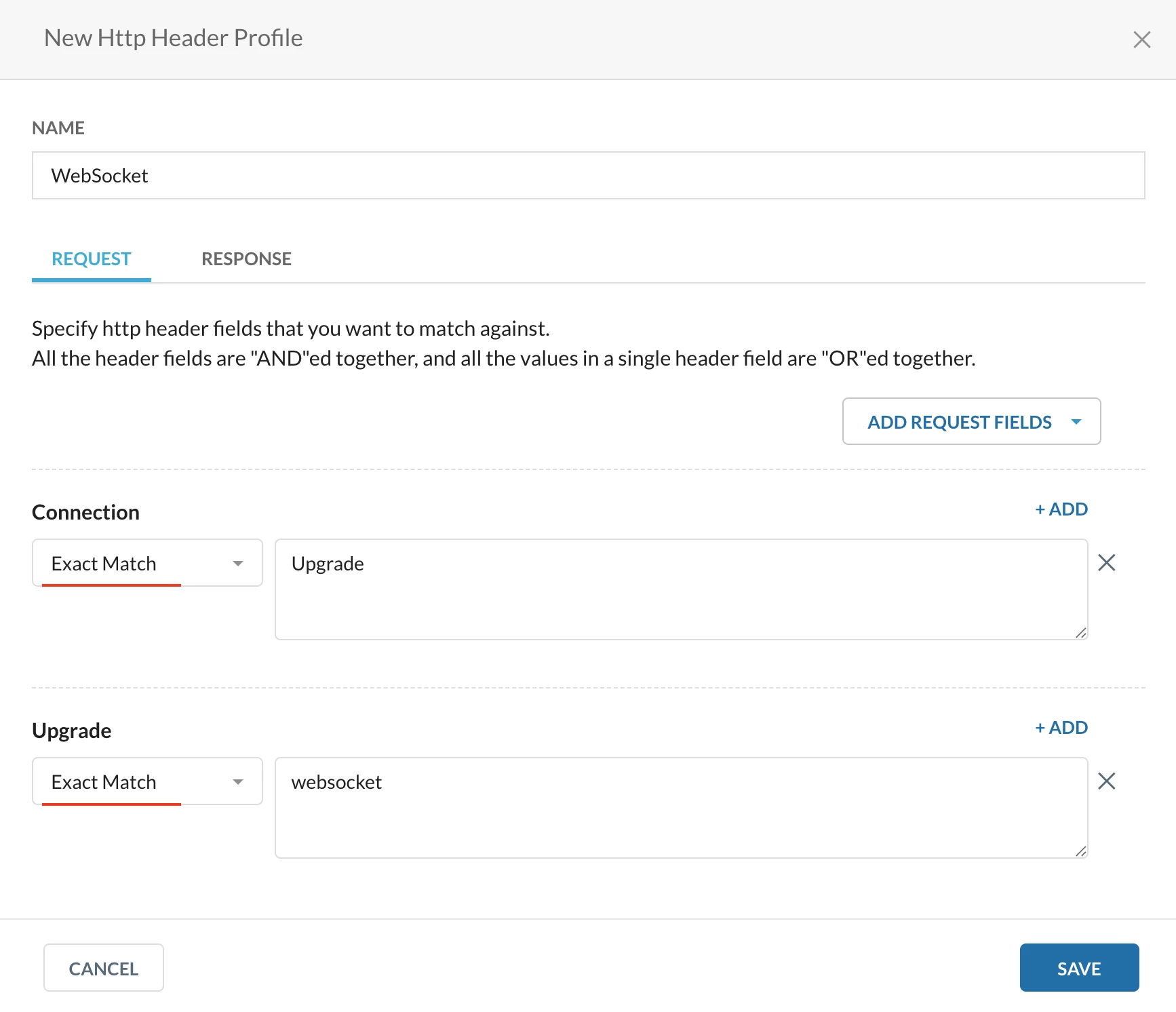
Step 1: Create a custom URL category
Path: Netskope Tenant UI >>> Policies >>> Profile - - - HTTP Header

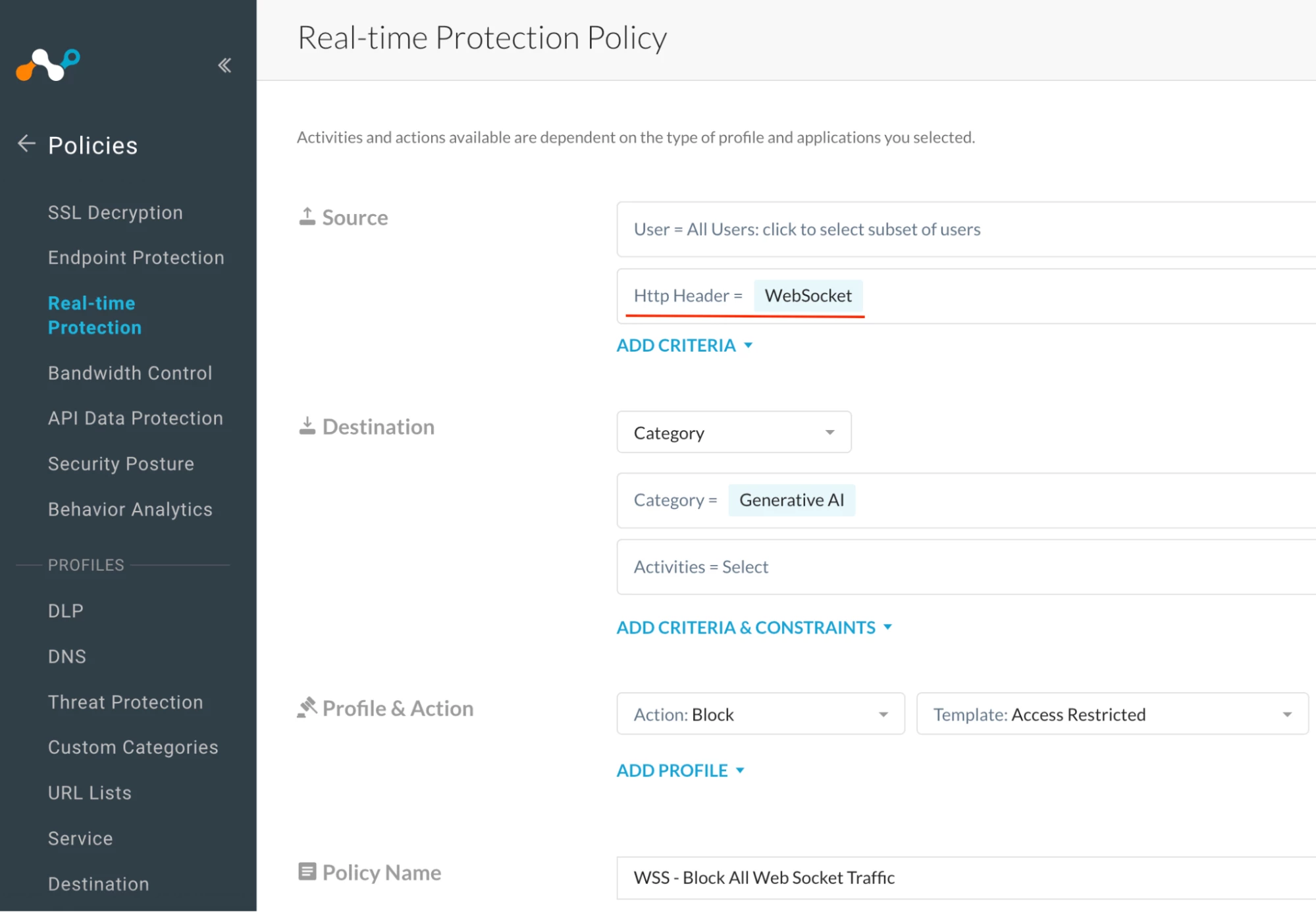
Step 2: Realtime protection policy
Path: Netskope Tenant UI >>> Policies >>> Real-time Protection >>> New Policy

Verification
Access Copilot via https://www.bing.com/
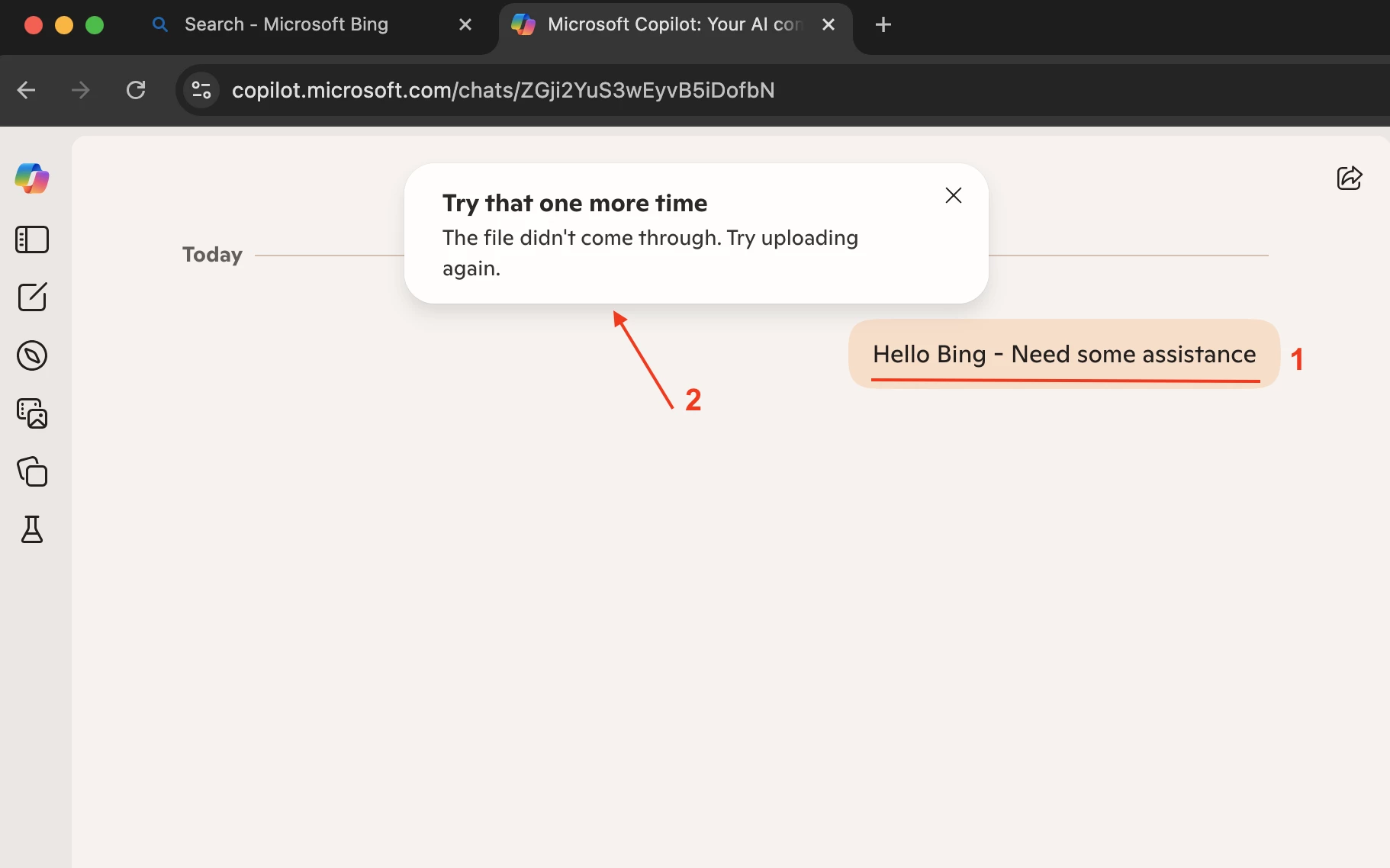

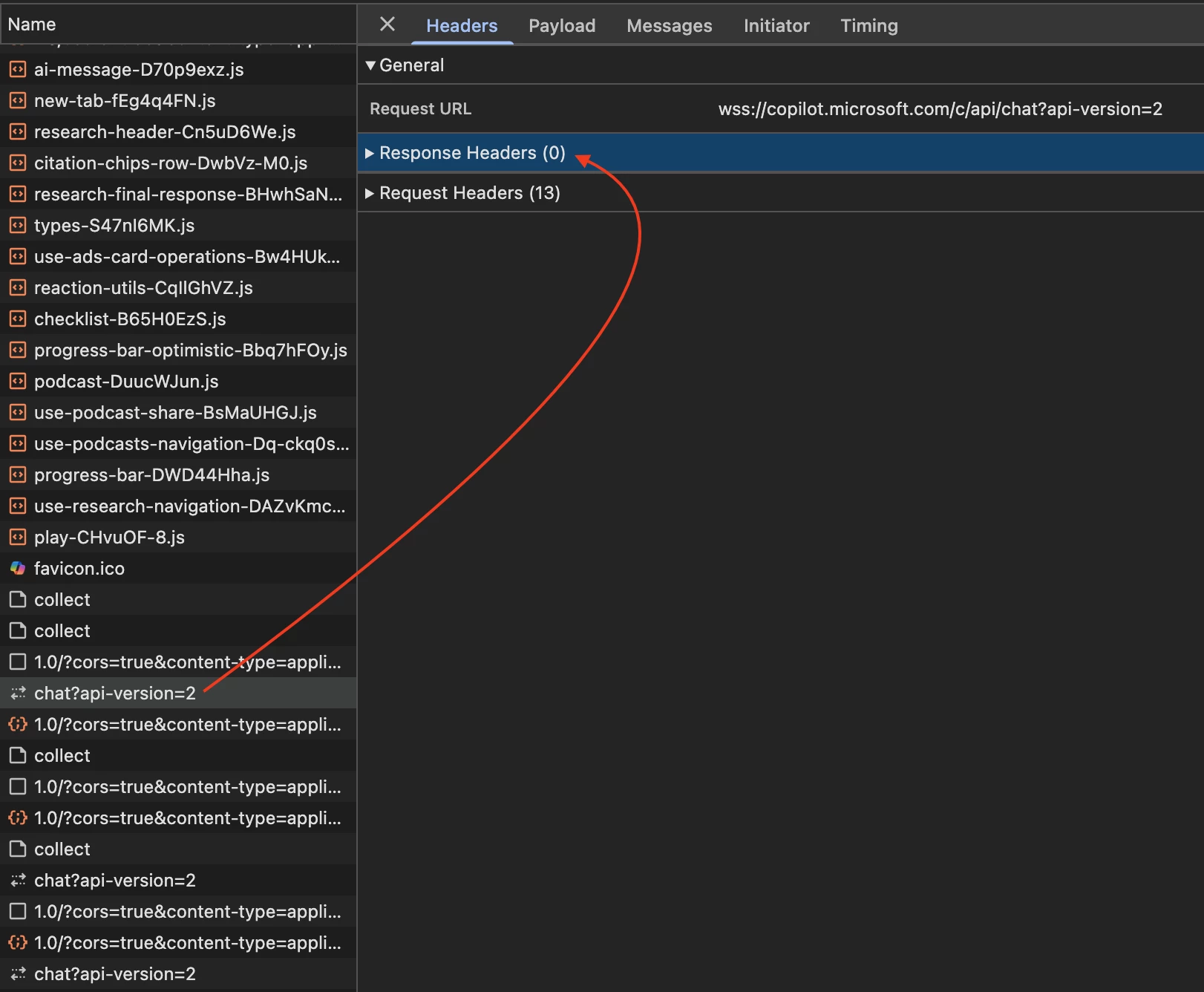

Note - We applied the controls on the HTTP Request Header, which is why the query receives no response — the request header is being blocked. There is no user notification in this scenario because the wss:// connection runs as a backend service in the application.
Author Notes
Q: Why does an application switch from HTTPS to WSS?
A: Applications switch from HTTPS to WSS for one main reason: Because WSS provides real-time, two-way communication that HTTPS cannot.
HTTPS is request–response
The browser must request data every time.
WSS keeps a persistent open connection, allowing:
real-time chat
instant notifications
typing indicators
live dashboards
AI model responses (like Copilot)
And,
Full-duplex communication
With HTTPS:
Client → Server only (no server-initiated push)
With WSS:
Client ⇄ Server both ways
Server can push updates instantly
Q: Name a few common applications that use WebSockets.
A: Details are below -
Copilot
Slack
MS Teams (web)
Salesforce Live Agent
Trading dashboards
Gaming platforms
- The HTTP header–based solution discussed above has been tested only with Copilot. Its behavior on other applications has not yet been validated. If it does not work as expected for other applications, kindly contact Netskope Customer Support for further assistance.
- When applying WebSocket-blocking controls company-wide, it is recommended that customers first test the policy with a few test users for a few weeks to validate the results. Some business applications may use WebSockets on the backend without the customer’s awareness.
Terms and Conditions
- All documented information undergoes testing and verification to ensure accuracy.
- In the future, it is possible that the application's functionality may be altered by the vendor. If any such changes are brought to our attention, we will promptly update the documentation to reflect them.
Notes
- This article is authored by Netskope Global Technical Success (GTS).
- For any further inquiries related to this article, please contact Netskope GTS by submitting a support case with 'Case Type – How To Questions'.







